As Pure as Synthetic, but Natural!
Cannabinoids are a class of diverse chemical compounds found in the cannabis plant. The most well-known of these is THC, which has been used as an active ingredient for the antiemetic drug Marinol, which was approved in the US by the FDA in 1985. Research has revealed that THC has an alleviating effect on chronic pain due to injury, surgery or illness. THC is the primary ingredient in the cannabis plant which leads to psychoactive effects and hence creates euphoria and giddiness, but also anxiety and paranoia.
CBD (cannabidiol) is another relatively well researched cannabinoid which has a wide spectrum of potential applications and is non-psychoactive. CBD is used to treat chronic pain, anxiety, spasticity, seizures, osteoporosis and a number of other conditions.
The advantage of using CBD/THC as primary pain relief ingredients is that they work both centrally (CB-1 receptors) as well as peripherally (CB-2 receptors). When an injury occurs, glial cells are increasingly produced around neurojunctions (synapses). These glial cells produce cytokines, chemical transmitters that induce inflammation and signal pain. When cannabinoids (CBD/THC) bind to the glial cell, the cytokine production decreases and the patient feels a remarkable decrease in chronic pain.
So far only synthetic cannabinoids (THC and CBD) were used in the US in drug products (Marinol and its generic versions) and drug candidates. Recently US FDA approved Epidolex (GW Pharma), which contained natural CBD.
Outside the US only natural cannabinoids are used in marketed drug product Sativex (GW Pharma)
The Endocannabinoid System
Endocannabinoids and their receptors are found throughout the body: in the brain, all organs, connective tissues, glands, and immune cells. In each tissue, the cannabinoid system performs different tasks, but the goal is always the same: homeostasis, the maintenance of a stable internal environment despite fluctuations in the external environment.
Cannabinoids promote homeostasis at every level of biological life, from the sub‐cellular, to the organism, and beyond. Endocannabinoids and cannabinoids are found at the intersection of the bodyʹs various systems, allowing communication and coordination between different cell types. At the site of an injury, for example, cannabinoids can be found decreasing the release of activators and sensitizers from the injured tissue, stabilizing the nerve cell to prevent excessive firing, and calming nearby immune cells to prevent release of pro‐inflammatory substances.
Emerging Clinical Applications
With this knowledge of the widespread action of cannabinoids within all bodily systems, it becomes much easier to conceptualize how the various forms of cannabinoids might have a potentially therapeutic effect on diseases ranging from osteoarthritis to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
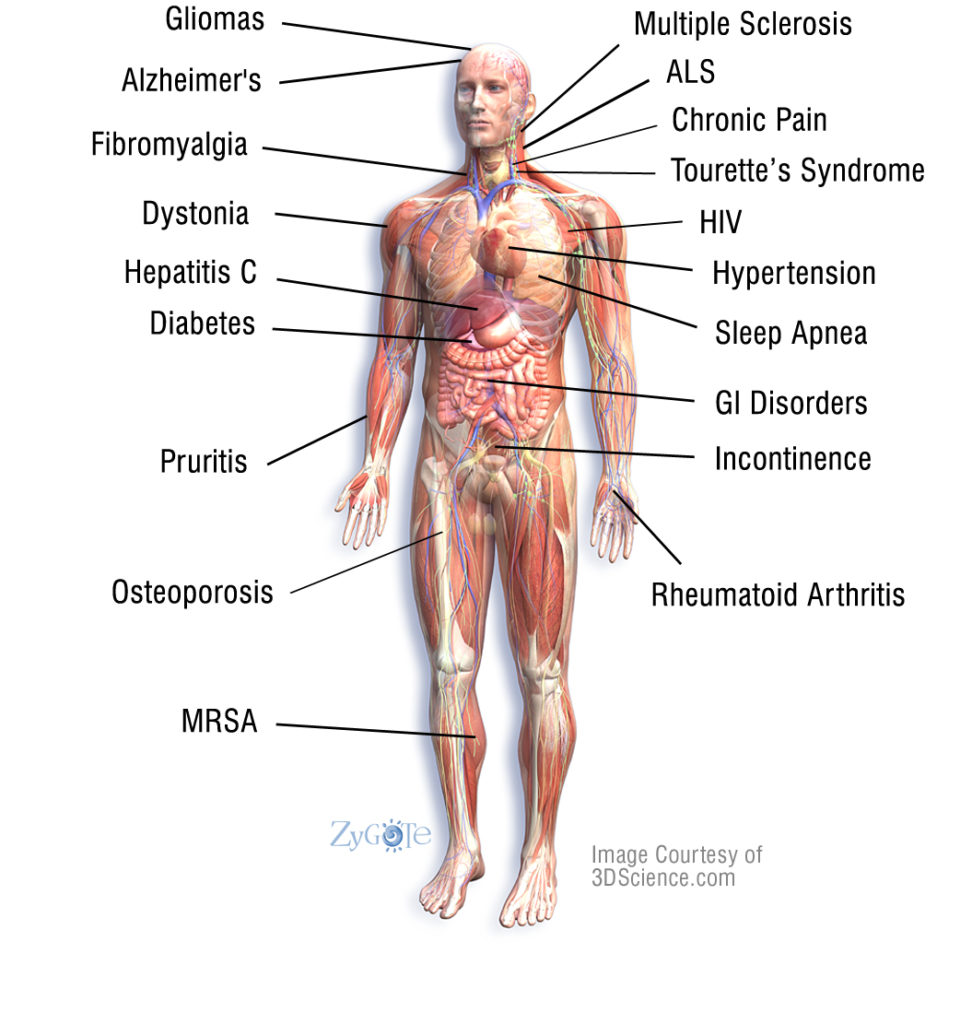 Writing in the September 2007 issue of the British Journal of Pharmacology, investigators at Irelandʹs Trinity College Institute of Neuroscience concluded, ʺ…cannabinoids offer a multi‐faceted approach for the treatment of Alzheimerʹs disease by providing neuroprotection and reducing neuroinflammation, whilst simultaneously supporting the brainʹs intrinsic repair mechanisms by augmenting neurotrophin expression and enhancing neurogenesis…Manipulation of the cannabinoid pathway offers a pharmacological approach for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease that may be more efficacious than current treatment regimens.ʺ
Writing in the September 2007 issue of the British Journal of Pharmacology, investigators at Irelandʹs Trinity College Institute of Neuroscience concluded, ʺ…cannabinoids offer a multi‐faceted approach for the treatment of Alzheimerʹs disease by providing neuroprotection and reducing neuroinflammation, whilst simultaneously supporting the brainʹs intrinsic repair mechanisms by augmenting neurotrophin expression and enhancing neurogenesis…Manipulation of the cannabinoid pathway offers a pharmacological approach for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease that may be more efficacious than current treatment regimens.ʺ
Therapeutic Effects
Global Wound Care Industry
Certain cannabinoids, in particular CBG (cannabigerol) are known to have very strong antibacterial and antifungal properties. They have been proven active in treatment of MRSA and CRB. Cannabinoids are potent anti-inflammatory and immunomodulating agents and as such have unique applicability in wound care and MRONJ in particular.
According to RnR Market Research, the global wound care market size will reach $22.01 billion by 2022 from $18.35 billion in 2017 driven by the increasing prevalence of surgical wounds & ulcers (diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous congestion leg ulcers), increasing aging population, increasing demand for evidence-based advanced wound care products, rising R&D activities, progress in the field of advanced wound care research and increasing awareness about wound care treatment. The advanced wound care category will grow at a faster rate than that of non-advanced wound care.
Geographically, the advanced wound care market is dominated by North America, followed by Europe in 2017. The Asia Pacific region is estimated to grow at the fastest rate which can be attributed to the large population in China and India, increasing research in wound care, and increasing penetration of key players in the emerging markets of Asia Pacific.
Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is a severe adverse drug reaction, consisting of progressive bone destruction in the maxillofacial region. MRONJ adversely affects the quality of life and results in significant morbidity and mortality.
Thus, in view of the very limited options for any effective treatment, addressing the causes and symptoms of the debilitating MRONJ furthermore strongly depends on the judgement of the disease stage of the patient. APIRx is developing clinical strategies for both prophylaxis and treatment of MRONJ based on certain cannabinoids with known anti-inflammatory, anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties.